Plosives can be a frustrating issue in audio recordings, causing distracting popping or windy sounds when certain breath-heavy consonants are pronounced. While it’s best to avoid plosives during recording, there are techniques to eliminate plosives during post-production. This article will discuss effective methods for removing plosives and achieving clear and high-quality audio.
One technique is using filters like low-cut or high-pass filters to attenuate the bass frequencies that plosives occupy. Another option is using a dynamic EQ to selectively attenuate plosives in the frequency range. Additionally, specialized tools like iZotope’s RX De-Plosive and RX 10 Advanced can provide advanced features for precise plosive removal.
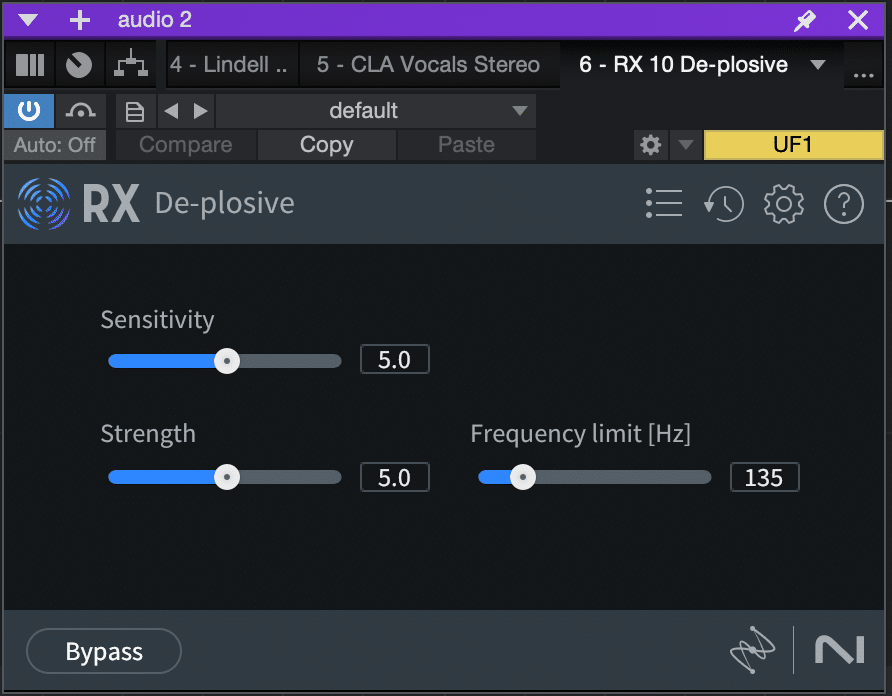
Izotope RX De-Plosive
But prevention is always better than cure. Proper mic placement, the use of pop filters, and employing a low roll-off before compression can help prevent plosives during the recording process. By implementing these best practices, you can minimize the need for extensive plosive removal in post-production.
Key Takeaways:
- Plosives are a common issue in audio recordings caused by excessive air pressure on the microphone’s capsule.
- Techniques like using filters and dynamic EQ can effectively remove plosives during post-production.
- Specialized tools like iZotope’s RX De-Plosive and RX 10 Advanced provide advanced features for precise plosive removal.
- Preventing plosives during the recording process through proper mic placement and the use of pop filters is ideal.
- It’s important to find the right balance between plosive removal and preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal.
Understanding Plosives
Plosives are consonant sounds that occur when the air from the vocalist hits the microphone’s capsule with excessive force, resulting in a popping or booming sound. Common examples of plosives are the “Pa,” “Ba,” and “Fa” sounds.
The main causes of plosives are the release of air during the pronunciation of certain consonants, particularly those that require a heavy breath. When these sounds are produced, the forceful burst of air can overload the microphone’s capsule and create unwanted audio artifacts.
To better understand plosives, it’s helpful to consider their phonetic classification. Plosives, also known as stop consonants, are characterized by a complete blockage of airflow in the vocal tract followed by a sudden release. This results in a sharp burst of sound and air pressure that can cause issues in recordings.
In order to effectively eliminate plosives from recorded audio, it’s important to have a clear understanding of their nature and how they are formed. By recognizing the specific sounds that contribute to plosives and the underlying causes, we can implement strategies to minimize their impact and ensure clean, professional-quality recordings.
“Plosives are consonants that haoppen when the air from the vocalist hits the microphone’s capsule with excessive force, resulting in a popping or booming sound.” – Matty Harris
Removing Plosives with Filters
One effective technique for removing plosives from recorded audio is to use filters. By using low-cut filters or high-pass filters, it is possible to attenuate the bass frequencies that plosives typically occupy. This helps in reducing the energy of the plosive, resulting in a less noticeable pop or boom sound. It is important to exercise caution while implementing this technique to avoid cutting too much of the vocal’s natural low end, which can adversely affect the overall sound quality. To achieve a more precise reduction of plosives, it is recommended to use a 24dB per octave slope. The implementation of filters can significantly enhance the audio quality by eliminating plosives in post-production.
In addition, I would like to highlight an important point for consideration. While filters are effective in removing plosives, they may also impact the overall frequency balance of the audio. Striking the right balance between plosive reduction and preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal is crucial. It is essential to make adjustments and fine-tune the filter parameters to achieve the desired result without introducing any unwanted artifacts.
Using low-cut filters, high-pass filters, and other plosive removal techniques in audio post-production can greatly enhance the quality of recorded sound. The application of these techniques allows for the reduction of plosives, resulting in clear and professional audio output.
Quotes:
“My favorite tool for removing plosives is Izotope’s RX De-Plosive plugin. I use it as an AudioSuite Plugin in Pro Tools or as an Event FX in Studio One
” – Audio Engineer, Matty Harris
Understanding the appropriate usage and implementation of filters is essential for effective plosive removal. By incorporating this technique into your workflow, you can achieve high-quality audio that is free from distracting plosives.
List:
- Low-cut filters and high-pass filters are effective in reducing plosives.
- Cutting bass frequencies up to around 120Hz helps in attenuating plosive energy.
- Exercise caution to avoid cutting too much of the vocal’s natural low end.
- Using a 24dB per octave slope enables precise reduction of plosives.
- Fine-tuning filter parameters is crucial to strike the right balance between plosive reduction and preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal.
Table:
| Filter Type | Usage | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Low-cut filter | Attenuates frequencies below a set threshold | Highly effective in reducing plosives |
| High-pass filter | Allows frequencies above a set threshold to pass through | Effective in minimizing plosives |
Attenuating Plosives with Dynamic EQ
Another effective technique for reducing plosives in recorded audio is using a dynamic EQ. This specialized tool allows for precise control over the specific frequencies occupied by plosives, while preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal.
A dynamic EQ works by setting a threshold that determines when the EQ will be activated to attenuate the plosives. By adjusting the sensitivity and strength parameters, you can fine-tune the dynamic EQ to only trigger when plosives occur, effectively reducing their impact on the audio.
While a dynamic EQ may not always be as straightforward as using a low-cut filter, it offers a more nuanced approach to plosive removal. By targeting the specific frequency range of the plosives, you can minimize their presence without compromising the overall sound quality.
The key to successful plosive reduction with a dynamic EQ lies in careful threshold settings. Setting the threshold too high may result in incomplete removal of plosives, while setting it too low may introduce unwanted artifacts and affect the natural timbre of the vocal. It’s essential to experiment with different threshold levels to find the right balance for your particular recording.
When utilizing a dynamic EQ, it’s important to take into account the preservation of vocal characteristics. Unlike other methods that may lead to a loss of natural tone, a dynamic EQ allows for more targeted control, ensuring that the vocal’s unique qualities are maintained while addressing plosives.
“By using a dynamic EQ, I was able to precisely attenuate the plosives in the recording, while preserving the vocalist’s raw and emotive performance. It’s an invaluable tool for achieving a clean and natural-sounding audio without compromising the artistic integrity of the vocal.”
Dynamic EQs are available as standalone plugins or as part of comprehensive audio processing software. Some popular options include Waves F6 Floating-Band Dynamic EQ, Universal Audio Precision EQ, and FabFilter Pro-Q 3. These plugins offer advanced features and user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible to both beginners and experienced audio engineers.
While a dynamic EQ may not always be the go-to choice for plosive removal, it provides an effective alternative when preserving vocal characteristics is of utmost importance. By exploring the capabilities of a dynamic EQ and optimizing threshold settings, you can achieve professional-quality audio free from distracting plosives.
Specialized Tools for Plosive Removal
When it comes to removing plosives from audio recordings, specialized tools can greatly simplify the process. One such tool that stands out in the industry is iZotope’s RX De-Plosive. This plugin is specifically designed to tackle the challenge of plosive removal, offering precise control over plosive attenuation. By using RX De-Plosive, audio engineers and producers can effectively eliminate plosives and ensure a clean, professional sound.
It’s worth noting that RX De-Plosive is part of iZotope’s comprehensive RX suite, a collection of advanced audio repair tools used by industry-leading professionals. This means that you can integrate RX De-Plosive seamlessly with other plugins from the suite to tackle a wide range of audio issues beyond plosive removal. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, iZotope’s RX De-Plosive offers a reliable and effective solution for plosive removal.
Another impressive option for plosive removal is RX 10 Advanced, an award-winning audio repair suite trusted by post-production engineers worldwide. This comprehensive software provides a suite of powerful tools and functionalities for repairing and enhancing audio recordings. With RX 10 Advanced, you have access to advanced features that allow for precise plosive removal while preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal.
Using iZotope’s RX De-Plosive or the RX 10 Advanced suite, you can confidently address plosives in your audio recordings, ensuring optimal sound quality and clarity. These specialized tools offer professional-grade solutions for plosive removal, empowering audio professionals to deliver impeccable results in their projects.

One of my Favorite De-essers is the Weiss Desser from Softube. I always use the Vocal two-band Control Preset. – Matty Harris
Best Practices for Preventing Plosives
While post-production techniques can help eliminate plosives, it’s always best to prevent them during the recording process. By following these best practices, you can minimize the need for extensive plosive removal in post-production.
-
Mic Placement
Proper mic placement is crucial for preventing plosives. Ensure that the vocalist’s breath doesn’t directly hit the microphone’s capsule. Position the microphone slightly above or below the vocalist’s mouth, angled slightly off-axis to capture the vocals while minimizing the direct impact of breath. This positioning can help reduce the occurrence of plosives by avoiding direct air pressure on the microphone.
-
Pop Filters
Using pop filters or windscreens can be highly effective in minimizing plosives. These devices are specifically designed to diffuse the blast of air from plosive sounds, reducing their impact on the microphone. Place the pop filter about two inches in front of the microphone, positioning it between the vocalist and the microphone’s capsule. This physical barrier helps to disperse the air pressure and prevents it from directly hitting the microphone, resulting in cleaner audio with fewer plosives.
-
Techniques for Preventing Plosives
Employing a low roll-off before compression can also help prevent plosives from being captured during the recording process. A low roll-off filter reduces the low-frequency content in the vocal signal before it reaches the compressor, minimizing the chances of plosives triggering excessive compression. This technique can be effective in reducing plosives without compromising the vocal quality.
By implementing these best practices, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of plosives during recording. Proper mic placement, the use of pop filters, and employing a low roll-off filter are key techniques for preventing plosives and ensuring clean and high-quality audio.
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mic Placement | – Minimizes direct air pressure on the microphone – Preserves natural vocal characteristics |
– Requires careful positioning for optimal results – Might not completely eliminate plosives in all cases |
| Pop Filters | – Effectively diffuses air pressure from plosives – Easy to use and affordable |
– Can slightly affect the overall frequency response – May require frequent cleaning or replacement |
| Low Roll-Off Filter | – Reduces plosive occurrence before compression – Preserves vocal characteristics |
– May affect low-frequency content in the vocal – Requires proper adjustment based on the vocalist’s voice |
Common Challenges and Side Effects
While there are effective techniques for removing plosives, it’s important to be aware of the potential challenges and side effects that may arise. One of the main challenges is finding the right balance between reducing plosives and preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal. It can be a delicate process, as cutting too much of the low end in an attempt to remove plosives can result in an unnatural sound.
Additionally, certain plosive removal techniques, such as using low-cut filters, have the potential to affect the overall frequency balance of the audio. These filters primarily target the bass frequencies, which are often occupied by plosives. However, the trade-off is that other elements in the recording, such as the vocal’s natural warmth or depth, may also be affected.
It’s crucial to use plosive removal techniques judiciously and make adjustments to achieve the desired result without introducing new issues. Careful attention should be paid to the overall frequency balance and sonic integrity of the audio, ensuring that the removal of plosives does not compromise the quality and naturalness of the vocal.
“Achieving a perfect balance between plosive removal and preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal is an ongoing challenge. It requires a keen ear and meticulous fine-tuning to ensure a clean and clear audio without sacrificing the authenticity of the performance.” – Audio Engineer
Side Effects of Plosive Removal Techniques
When employing plosive removal techniques, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects that may arise. These side effects can vary depending on the specific technique used and the characteristics of the recording.
One common side effect of using low-cut filters for plosive removal is the potential loss of low-frequency content. While the filters are effective at attenuating plosives, they can also unintentionally remove desired low-frequency elements, impacting the overall warmth and fullness of the recording.
Dynamic EQ, another technique for plosive removal, can introduce side effects if not properly set up. Incorrectly adjusting the threshold settings may result in unnatural changes in volume or tone during the vocal performance. It’s important to carefully calibrate the dynamic EQ parameters to avoid noticeable artifacts or inconsistencies in the audio.
Overall, understanding and mitigating the potential side effects of plosive removal techniques is crucial in maintaining the quality and integrity of the recorded audio. A comprehensive approach that includes careful adjustments, monitoring, and testing can help minimize these side effects and achieve optimal results.
| Potential Challenges | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Finding the right balance between reducing plosives and preserving natural vocal characteristics | Loss of low-frequency content due to low-cut filters, unnatural volume or tone changes with dynamic EQ |
| Affecting the overall frequency balance of the audio | Unintentional removal of desired low-frequency elements, noticeable artifacts or inconsistencies in the audio |
Conclusion
Plosives can be a common issue in recorded audio, causing distracting pops and booms. However, there are effective techniques to remove these plosives and achieve clear and high-quality audio. Using filters such as low-cut or high-pass filters, and dynamic EQ can significantly attenuate plosives in post-production. Specialized tools like iZotope’s RX De-Plosive and RX 10 Advanced provide advanced features for precise plosive removal.
While these techniques are helpful, it’s always best to prevent plosives during the recording process. Proper mic placement, where the vocalist’s breath doesn’t directly hit the microphone’s capsule, is crucial. Using pop filters or windscreens can also help diffuse the blast of air and minimize plosives. By employing these techniques and best practices, you can minimize the need for extensive plosive removal in post-production and maintain the natural characteristics of the vocal.
With a focus on prevention and the use of effective techniques for plosive removal, you can ensure clear, high-quality audio free from the distracting presence of plosives. By addressing plosives both during recording and in post-production, you can deliver professional-sounding audio that captivates your audience.
If you would like me to fix your plosives feel free to get in touch.
FAQ
What are plosives?
Plosives are consonant sounds that occur when the air from the vocalist hits the microphone’s capsule with excessive force, resulting in a popping or booming sound.
What causes plosives?
Plosives are mainly caused by the release of air during the pronunciation of certain consonants, particularly those that require a heavy breath.
Can plosives be removed during post-production?
Yes, plosives can be removed during post-production using various techniques such as filters and dynamic EQs.
How can I remove plosives using filters?
You can remove plosives using filters like low-cut or high-pass filters to attenuate the bass frequencies typically occupied by plosives.
What is a dynamic EQ and how can it help with plosive removal?
A dynamic EQ allows for targeted attenuation of the specific range of frequencies occupied by plosives. It helps preserve the natural vocal characteristics while reducing plosives.
Are there any tools specifically designed for plosive removal?
Yes, tools like iZotope’s RX De-Plosive and RX 10 Advanced are designed specifically for plosive removal in audio recordings.
How can I prevent plosives during recording?
You can prevent plosives during recording by implementing proper mic placement, using pop filters or windscreens, and employing a low roll-off before compression.
What are the challenges and side effects of plosive removal techniques?
One challenge is finding the right balance between reducing plosives and preserving the natural characteristics of the vocal. Some removal techniques may also affect the overall frequency balance of the audio.
What is the summary of plosive removal techniques?
The key techniques for plosive removal include using filters, dynamic EQs, and specialized tools. It’s important to prevent plosives during recording and use these techniques judiciously.